Table of Contents
ToggleSensex: The Pulse of India’s Stock Market
When someone mentions the stock market in India, the word Sensex inevitably comes up. It’s more than just a number flashing on your screen—it’s a reflection of the Indian economy, investor sentiment, and market momentum. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a curious beginner, understanding Sensex is key to grasping how India’s financial heartbeat functions.

But what exactly is Sensex? Why does it rise and fall? And how can you make sense of it in your investment journey?
Let’s dive deep.
What Is Sensex? A Brief Overview
Sensex, or the S&P BSE Sensex, is the benchmark stock market index of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), one of India’s oldest and most prominent stock exchanges. Launched in 1986, it tracks 30 of the largest and most financially sound companies listed on the BSE.
These 30 companies span major sectors like finance, IT, FMCG, oil & gas, and more—providing a snapshot of India’s economic landscape. When the Stock market gauge rises, it typically signals optimism and economic strength. When it falls, it may suggest investor caution or market turmoil.
Some Fast Facts About Sensex:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | S&P BSE Sensex |
| Launch Year | 1986 |
| Number of Stocks | 30 |
| Base Year | 1978–79 |
| Base Value | 100 |
| Exchange | Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) |
How Does Sensex Work?
Stock market gauge is a market-capitalization-weighted index. This means that the weight of each company in the index is based on its total market value. So, larger companies like Reliance Industries, TCS, or HDFC Bank have a bigger impact on the Stock market gauge than smaller ones.
Formula Used:
The Stock market gauge is calculated using the Free-Float Market Capitalization Method, which excludes shares held by promoters, government, or strategic investors, focusing only on shares available for public trading.
This provides a more accurate representation of the market’s real movements based on active trading.
Why Is Sensex So Important?
The Stock market gauge acts as the barometer of India’s economy and investor sentiment. Here’s why it matters:
-
Investor Confidence: A rising Stock market gauge attracts more retail and institutional investors, both domestic and global.
-
Economic Health: It mirrors macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and fiscal policies.
-
Benchmarking Tool: Mutual funds and portfolio managers compare their performance against the Sensex.
-
Global Recognition: Foreign investors track Stock market gauge to gauge opportunities in India.
Sensex vs Nifty: What’s the Difference?
While Stock market gauge is the BSE’s benchmark index, Nifty 50 is the National Stock Exchange’s (NSE) flagship index.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Sensex | Nifty 50 |
|---|---|---|
| Exchange | Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) | National Stock Exchange (NSE) |
| Launched | 1986 | 1996 |
| Companies | 30 | 50 |
| Base Year | 1978-79 | 1995 |
| Calculation Method | Free Float Market Cap | Free Float Market Cap |
👉 Want more about Nifty 50? Check out our Nifty 50 guide.
Historical Performance of Sensex: A Journey of Growth
From its base value of 100 in 1979, Stock market gauge has climbed to over 70,000 in recent years—showcasing India’s economic transformation. But it hasn’t been a smooth ride. There have been notable crashes and booms, each teaching valuable lessons.
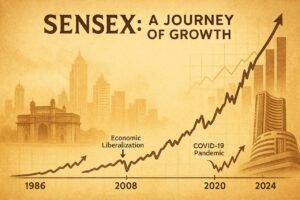
Major Milestones:
-
1992: Harshad Mehta scam causes a major crash.
-
2008: Global financial crisis drags Sensex below 10,000.
-
2020: COVID-19 pandemic causes panic selling.
-
2021-2024: Strong recovery, led by tech, banking, and consumption.
Pro Tip: Markets are volatile in the short run, but history shows a long-term uptrend in Stock market gauge.
What Affects the Sensex?
Understanding what moves the Stock market gauge can help you anticipate trends:
1. Economic Indicators
-
GDP Growth
-
Inflation
-
Interest Rates
-
RBI Policies
2. Corporate Earnings
-
Strong quarterly results boost investor confidence.
-
Weak results pull down stock prices, affecting the index.
3. Global Factors
-
US Federal Reserve interest rate decisions.
-
Geopolitical tensions like wars or trade conflicts.
-
Foreign institutional investor (FII) flows.
4. Budget Announcements
-
Government’s fiscal spending and tax reforms directly impact sectors like infra, banking, and manufacturing.
Sensex as an Investment Tool
While you can’t directly buy the Stock market gauge, you can invest in its movement through various vehicles:
1. Index Mutual Funds
They replicate the Stock market gauge portfolio and are ideal for passive investors.
2. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
ETFs like SBI ETF Sensex or HDFC Sensex ETF offer real-time trading flexibility.
3. Derivatives
For advanced traders, Sensex Futures and Options allow speculation on future movements.
Should You Rely Solely on Sensex for Investing?
Not really. While Sensex gives a broad view, it doesn’t cover:
-
Mid-cap and small-cap opportunities
-
Sectoral diversification
-
New-age tech startups or companies not in the top 30
Still, it’s a great starting point for building a low-risk, long-term portfolio.
My Personal Experience with Sensex
I started investing during the COVID-19 crash in March 2020. The Stock market gauge had plummeted below 30,000. Panic was everywhere. But instead of running, I began buying quality stocks and index funds regularly.
Three years later, not only did the market recover, but my portfolio grew substantially.
Lesson? Market downturns are opportunities in disguise—if you stay patient and informed.
Sensex in 2025: What Lies Ahead?
Experts predict continued volatility in the short term due to:
-
Global recession fears
-
Oil price instability
-
Elections in major economies
But India’s structural growth story—rising middle class, digital transformation, and strong reforms—remains intact. Many analysts see Sensex touching 85,000–90,000 levels in the next few years.
Keep a long-term horizon and avoid panic trading during dips.
Key Takeaways
| Topic | Insights |
|---|---|
| Sensex Definition | Benchmark index of BSE tracking 30 major companies |
| Role | Economic barometer, investor sentiment tracker |
| Movement Factors | Macros, earnings, global events, budget |
| Investment Options | Index funds, ETFs, derivatives |
| Strategy | Long-term focus, diversified portfolio |
Conclusion: Making Sense of Sensex
Stock market gauge isn’t just a financial metric—it’s a story of India’s resilience, economic evolution, and investor sentiment. Understanding it gives you a strategic advantage, whether you’re a casual observer or an active investor.
In today’s data-driven world, having a strong grip on indexes like the Stock market gauge can help you decode market narratives, make better decisions, and align your investments with long-term goals.
Call to Action
What’s your take on the Sensex?
Are you investing in index funds, or do you prefer stock picking?
Share your experience in the comments!
👉 Explore more:
Stay informed. Stay invested. 💹